
What Is a DASH Diet?
The DASH Diet is an eating plan created to support heart health, with a strong focus on lowering blood pressure. DASH stands for Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension, and the plan centers on whole foods, balanced nutrition, and consistent portion control rather than strict calorie tracking.
Healthcare professionals often recommend the DASH Diet because it promotes steady, sustainable habits. Instead of cutting out entire food groups, it encourages fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and low-fat dairy while limiting sodium, added sugars, and saturated fat. This structure makes the DASH Diet practical for long-term use.
Although the DASH Diet began as a tool for managing high blood pressure, many people follow it for broader health reasons. These include heart health, weight management, and overall dietary consistency. Its flexible framework allows people to adapt the plan to different lifestyles without extreme restrictions.

What Does DASH Stand For?
DASH stands for Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension. The name reflects the primary goal of the DASH Diet, which is to help reduce high blood pressure through consistent dietary choices rather than medication alone.
Researchers developed the DASH Diet after studying how specific foods affect blood pressure levels. They found that diets rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and low-fat dairy helped lower blood pressure more effectively than typical eating patterns high in sodium and saturated fat.
Although the original focus was hypertension, the DASH Diet extends beyond blood pressure control. Its structure supports overall heart health and encourages balanced nutrition without extreme restrictions. This broader appeal explains why the DASH Diet remains a common recommendation from doctors and registered dietitians.
How the DASH Diet Works
The DASH Diet works by emphasizing nutrient-dense foods that naturally support healthy blood pressure levels. Instead of counting calories or eliminating food groups, the plan focuses on daily and weekly servings from key categories such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy.
A core feature of the DASH Diet is its balance of nutrients like potassium, calcium, magnesium, fiber, and protein. These nutrients help regulate blood pressure and support cardiovascular health. At the same time, the diet limits sodium, added sugars, and saturated fat, which can contribute to higher blood pressure when consumed in excess.
The DASH Diet also promotes portion awareness. Serving sizes guide food intake without rigid tracking or apps. This approach helps people build steady eating habits that feel manageable over time, making the DASH Diet easier to maintain than highly restrictive plans.
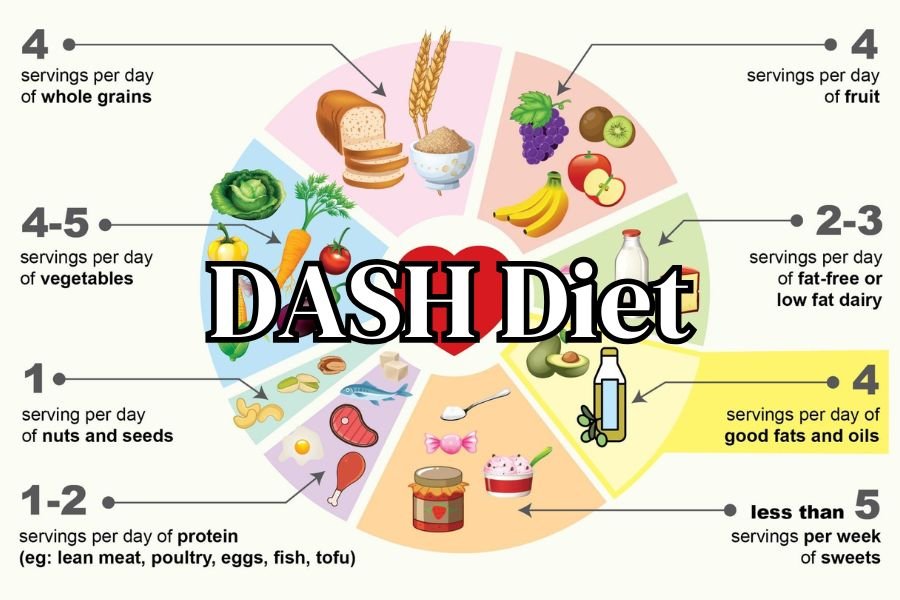
Foods You Eat on the DASH Diet
The DASH Diet emphasizes whole, minimally processed foods that provide steady nutrition throughout the day. Each food group plays a specific role, with clear serving recommendations to support balanced eating.
Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables form the foundation of the DASH Diet. They supply potassium, fiber, and antioxidants that help regulate blood pressure. Most plans recommend several servings per day, spread across meals and snacks. Common options include apples, berries, oranges, leafy greens, broccoli, carrots, and bell peppers.
Whole Grains
Whole grains provide energy and fiber while supporting digestive health. The DASH Diet favors foods such as whole wheat bread, brown rice, oats, quinoa, and whole grain pasta. These choices replace refined grains that often lack fiber and essential nutrients.
Lean Protein Sources
Protein supports muscle maintenance and satiety on the DASH Diet. Lean options include skinless poultry, fish, beans, lentils, and small portions of lean red meat. Plant-based proteins also play a strong role and help reduce saturated fat intake.
Low-Fat and Fat-Free Dairy
Low-fat and fat-free dairy products supply calcium and protein without excess saturated fat. Milk, yogurt, and cheese appear regularly in DASH Diet meal plans. These foods help support bone health while contributing to blood pressure control.
Nuts, Seeds, and Legumes
Nuts, seeds, and legumes add healthy fats, fiber, and plant protein. The DASH Diet includes these foods several times per week rather than daily. Examples include almonds, walnuts, sunflower seeds, chickpeas, and black beans.
Foods to Limit on the DASH Diet
The DASH Diet allows flexibility, but it sets clear limits on foods that can interfere with blood pressure control and heart health. Reducing these items helps the diet work more effectively.
High-sodium foods rank at the top of the list. Processed meats, canned soups, frozen meals, and packaged snacks often contain large amounts of salt. The DASH Diet encourages choosing fresh foods and reading nutrition labels to keep sodium intake in check.
Foods high in saturated fat also require moderation. Fatty cuts of meat, full-fat dairy products, butter, and fried foods can raise cholesterol levels. The DASH Diet favors lean protein and low-fat dairy to help manage fat intake.
Sugary drinks and sweets should remain occasional choices. Soda, sweetened tea, pastries, and candy add calories without meaningful nutrition. Limiting added sugars supports both heart health and weight management within the DASH Diet framework.
Highly processed and fast foods combine excess sodium, unhealthy fats, and added sugars. Regular consumption makes it harder to follow DASH Diet guidelines. Preparing meals at home allows better control over ingredients and portion sizes.
Sodium Guidelines on the DASH Diet
Sodium control plays a central role in the DASH Diet. Excess sodium can cause the body to retain fluid, which increases blood pressure. For this reason, the diet sets clear daily sodium limits.
The standard DASH Diet recommends no more than 2,300 milligrams of sodium per day, which aligns with general dietary guidelines. Many people see improvements in blood pressure at this level, especially when combined with higher intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
A lower-sodium version of the DASH Diet reduces intake further to 1,500 milligrams per day. Healthcare providers often suggest this option for people with hypertension, older adults, or those sensitive to sodium. This version requires closer attention to food labels and meal preparation.
Practical strategies help reduce sodium without sacrificing flavor. Cooking at home, using herbs and spices instead of salt, and choosing fresh or frozen vegetables over canned options make it easier to stay within DASH Diet sodium guidelines.
Health Benefits of the DASH Diet
The DASH Diet offers several well-documented health benefits, with blood pressure support being the most recognized. Research shows that following DASH Diet guidelines can lower systolic and diastolic blood pressure, often within a few weeks of starting the plan.
Heart health improves through reduced saturated fat, lower sodium intake, and higher consumption of fiber-rich foods. These changes help manage cholesterol levels and reduce strain on the cardiovascular system. As a result, many healthcare professionals recommend the DASH Diet for long-term heart support.
The DASH Diet can also support weight management. Although it does not focus on calorie restriction, its emphasis on whole foods and portion control helps reduce excess calorie intake naturally. Many people find it easier to maintain a steady weight while following the plan.
Blood sugar control is another benefit for some individuals. The DASH Diet prioritizes complex carbohydrates, lean protein, and fiber, which help stabilize energy levels and reduce sharp blood sugar spikes. This balanced approach may support people managing or aiming to prevent type 2 diabetes.
Who Should Follow the DASH Diet
The DASH Diet suits a wide range of people, especially those focused on heart health and blood pressure management. Doctors often recommend the plan for individuals diagnosed with high blood pressure or those at risk of developing it.
People with a family history of heart disease may also benefit from the DASH Diet. Its emphasis on whole foods, lean protein, and reduced sodium supports long-term cardiovascular health without extreme restrictions.
The DASH Diet also works well for individuals seeking a structured eating plan that feels realistic. Because it avoids strict rules and allows flexibility, it fits into many lifestyles. This makes it easier to maintain over time compared to more restrictive diets.
Although the DASH Diet suits most adults, anyone with specific medical conditions or dietary needs should consult a healthcare professional before making major changes. Personal guidance helps ensure the plan aligns with individual health goals.
Potential Downsides of the DASH Diet
The DASH Diet works well for many people, but it may present challenges for some. One common issue is the adjustment period. People accustomed to high-sodium or highly processed foods may find meals less flavorful at first. Taste preferences usually adapt over time.
Meal planning can also require extra effort. The DASH Diet relies on fresh ingredients and balanced meals, which may demand more time for grocery shopping and cooking. For individuals with limited schedules, this planning phase can feel inconvenient.
Some people may find the diet less suitable if they prefer very low-carbohydrate eating styles. The DASH Diet includes whole grains, fruits, and legumes, which increase carbohydrate intake compared to low-carb plans.
Cost can be another consideration. Fresh produce, lean protein, and low-fat dairy may cost more than processed alternatives. Careful planning, buying seasonal produce, and using frozen options can help manage expenses while staying within DASH Diet guidelines.
DASH Diet vs Other Popular Diets
The DASH Diet often draws comparisons to other well-known eating plans. Each approach shares some similarities, but key differences affect how people follow them long term.
DASH Diet vs Mediterranean Diet
Both plans emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. The Mediterranean diet places greater emphasis on olive oil, seafood, and moderate alcohol intake, particularly wine. The DASH Diet includes more structured servings of low-fat dairy and sets clearer sodium limits, which makes it especially effective for blood pressure management. People who need defined sodium targets often prefer the DASH Diet.
DASH Diet vs Low-Carb Diets
Low-carb diets restrict grains, fruits, and some legumes to reduce carbohydrate intake. The DASH Diet includes these foods because they provide fiber, potassium, and magnesium, which support heart health. For people who prefer dietary balance rather than strict carbohydrate limits, the DASH Diet is easier to follow over time.
DASH Diet vs Keto Diet
The keto diet focuses on very low carbohydrate intake and high fat consumption. In contrast, the DASH Diet limits saturated fat and encourages complex carbohydrates. The DASH Diet supports steady energy levels and does not require ketosis, making it more suitable for long-term cardiovascular health.
DASH Diet vs Calorie-Counting Diets
Calorie-based diets rely on tracking daily intake, which can feel restrictive or time-consuming. The DASH Diet uses food group servings and portion awareness instead. This approach reduces the need for constant tracking while still encouraging consistent eating habits.
DASH Diet vs Plant-Based Diets
Plant-based diets may eliminate animal products entirely. The DASH Diet allows both plant and animal foods, including lean meats and low-fat dairy. This flexibility appeals to people who want structure without giving up familiar foods.
DASH Diet vs Weight Loss–Focused Diets
Some diets prioritize rapid weight loss through aggressive restrictions. The DASH Diet supports gradual weight changes by promoting balanced nutrition. This steady approach helps reduce the risk of nutrient deficiencies and supports long-term adherence.
Sample Day on the DASH Diet
A sample day on the DASH Diet shows how meals can stay balanced, filling, and low in sodium without feeling restrictive. Portions vary based on calorie needs, but the structure remains consistent.
Breakfast
Breakfast on the DASH Diet focuses on fiber, protein, and calcium to support steady energy.
- Rolled oats cooked with low-fat milk or unsweetened almond milk
- Fresh blueberries and sliced banana
- One tablespoon of chopped walnuts or almonds
- Coffee or tea without added sugar
This meal provides whole grains, fruit, and dairy while keeping sodium low.
Mid-Morning Snack
Snacks help prevent large swings in hunger.
- Low-fat Greek yogurt
- Or a medium apple with a small handful of unsalted nuts
Both options support DASH Diet guidelines and provide protein or fiber between meals.
Lunch
Lunch combines lean protein, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Grilled or baked chicken breast
- Large mixed green salad with tomatoes, cucumbers, and carrots
- Olive oil and lemon juice dressing
- One slice of whole grain bread or a serving of brown rice
Using herbs and citrus instead of salt keeps the meal within DASH Diet sodium targets.
Afternoon Snack
An afternoon snack maintains energy through the late part of the day.
- Raw vegetables such as carrots or bell peppers
- Hummus made with minimal added salt
This snack adds legumes and vegetables, both key components of the DASH Diet.
Dinner
Dinner rounds out the day with protein, vegetables, and complex carbohydrates.
- Baked salmon or roasted tofu
- Steamed broccoli or green beans
- Quinoa or roasted sweet potatoes
- Garlic, herbs, and spices for flavor
This meal supports heart health while meeting DASH Diet nutrient goals.
Evening Option (If Needed)
Some people prefer a small evening option.
- Fresh fruit
- Or warm low-fat milk
This helps manage hunger without excess calories or sodium.
A sample day like this shows how the DASH Diet supports balance across meals while remaining practical for everyday eating.
Tips for Starting the DASH Diet
Starting the DASH Diet works best with gradual changes rather than sudden shifts. Small adjustments help build consistency and reduce frustration during the first few weeks.
Begin by adding more fruits and vegetables to meals you already eat. This simple step increases potassium and fiber intake while naturally reducing space for higher-sodium foods. Over time, these additions align daily eating patterns with DASH Diet recommendations.
Plan meals ahead of time to stay organized. Creating a weekly grocery list based on DASH Diet food groups makes shopping easier and helps avoid impulse purchases. Preparing meals at home also gives better control over sodium and portion sizes.
Pay close attention to nutrition labels. Many packaged foods contain more sodium than expected. Choosing low-sodium or no-salt-added options supports DASH Diet guidelines without requiring major recipe changes.
Focus on progress rather than perfection. The DASH Diet allows flexibility, so occasional indulgences do not undo overall habits. Consistency over time matters more than following the plan perfectly every day.
Conclusion
The DASH Diet is a structured eating plan built around whole foods, balanced portions, and reduced sodium intake. It began as a strategy for lowering blood pressure, but its benefits extend to heart health, weight management, and overall dietary consistency.
By focusing on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and low-fat dairy, the DASH Diet promotes habits that are practical for long-term use. Its flexibility allows people to adapt meals to their preferences without extreme restrictions.
For individuals seeking a sustainable approach to healthy eating, the DASH Diet offers clear guidelines without rigid rules. With steady effort and thoughtful food choices, it can support lasting improvements in health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions About the DASH Diet
Is the DASH Diet good for weight loss?
The DASH Diet can support weight loss, even though it does not rely on calorie counting. Its focus on whole foods, fiber, and lean protein often reduces overall calorie intake naturally. Weight loss tends to occur at a steady pace when the plan is followed consistently.
Can vegetarians follow the DASH Diet?
Yes, the DASH Diet works well for vegetarians. Plant-based protein sources such as beans, lentils, tofu, nuts, seeds, and low-fat dairy fit easily within DASH Diet guidelines. Meals remain balanced without the need for meat.
How long does it take to see results on the DASH Diet?
Many people notice lower blood pressure within two to four weeks. Other changes, such as improved energy levels or weight shifts, may take longer. Results depend on sodium intake, food choices, and overall consistency with the DASH Diet.
How much sodium is allowed on the DASH Diet?
The standard DASH Diet limits sodium to 2,300 milligrams per day. A lower-sodium version reduces intake to 1,500 milligrams per day. Healthcare providers often recommend the lower limit for people with high blood pressure or sodium sensitivity.
Can I eat eggs on the DASH Diet?
Yes, eggs can fit into the DASH Diet when eaten in moderation. Eggs provide protein and important nutrients. Pairing them with vegetables and whole grains helps maintain balance within DASH Diet guidelines.
Is the DASH Diet safe for long-term use?
The DASH Diet is considered safe for long-term use by most adults. It does not eliminate major food groups and encourages balanced nutrition. Many healthcare professionals support it as a sustainable eating plan.
Does the DASH Diet require supplements?
The DASH Diet does not require supplements for most people. Its emphasis on nutrient-rich foods often meets daily vitamin and mineral needs. Supplements may be useful in specific cases, but professional guidance is recommended.
Can the DASH Diet help with cholesterol levels?
Yes, the DASH Diet may help improve cholesterol levels. Lower saturated fat intake and higher fiber consumption support healthy LDL cholesterol levels, which benefits heart health.
References
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (n.d.). DASH eating plan. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
- Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). DASH diet: Healthy eating to lower blood pressure. Mayo Clinic.
- Heart & Stroke. (n.d.). DASH diet.
- Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). DASH eating plan [PDF].
- Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). DASH diet: What it is, meal plans, and recipes.
- National Kidney Foundation. (n.d.). DASH diet.
- MedlinePlus. (n.d.). DASH eating plan. U.S. National Library of Medicine.




